Hi there ! I’m Mao who works for Home Nursing Station.
Vital signs are measurements of various parts of the body in order to objectively judge the life response that a human being is “alive”, and quantify this information.
This time, I will explain the purpose and specific method of measuring vital signs and also introduce useful skills in the field of Home Nursing.
Vital signs are closely related to physical assessment, so please also check related link on physical assessment.
- When checking vital signs immediately
- When the pulse is hard to recognize in the radial artery
- When blood pressure cannot be measured in the upper extremities
- When there is respiratory arrhythmia
- When SpO2 cannot be measured
- When the thermometer cannot be clamped
- When the body temperature is high despite of good physical condition
Measurement of Vital Signs

The purpose of measuring vital signs is to objectively judge whether the patient’s condition is normal.
Furthermore, another reason of measuring vital signs is to understand how the patient has changed since the last time of results.
Comprehensive evaluation of these items enables early detection of patient abnormalities.
Measurement Items of Vital Signs
There are measurement items of vital signs in below.
1, Pulse
2, Breathing
3, Blood Pressure
4, Body Temperature
5, SpO2 (Percutaneous Arterial Oxygen Saturation)
6, Urine Volume
Make sure you have a solid understanding of the basics of these items so that you can implement them properly.
Standard Values for Life-Threatening Vital Signs Measurements
The nurses have to understand the life-threatening standard values for each vital signs measurement items.
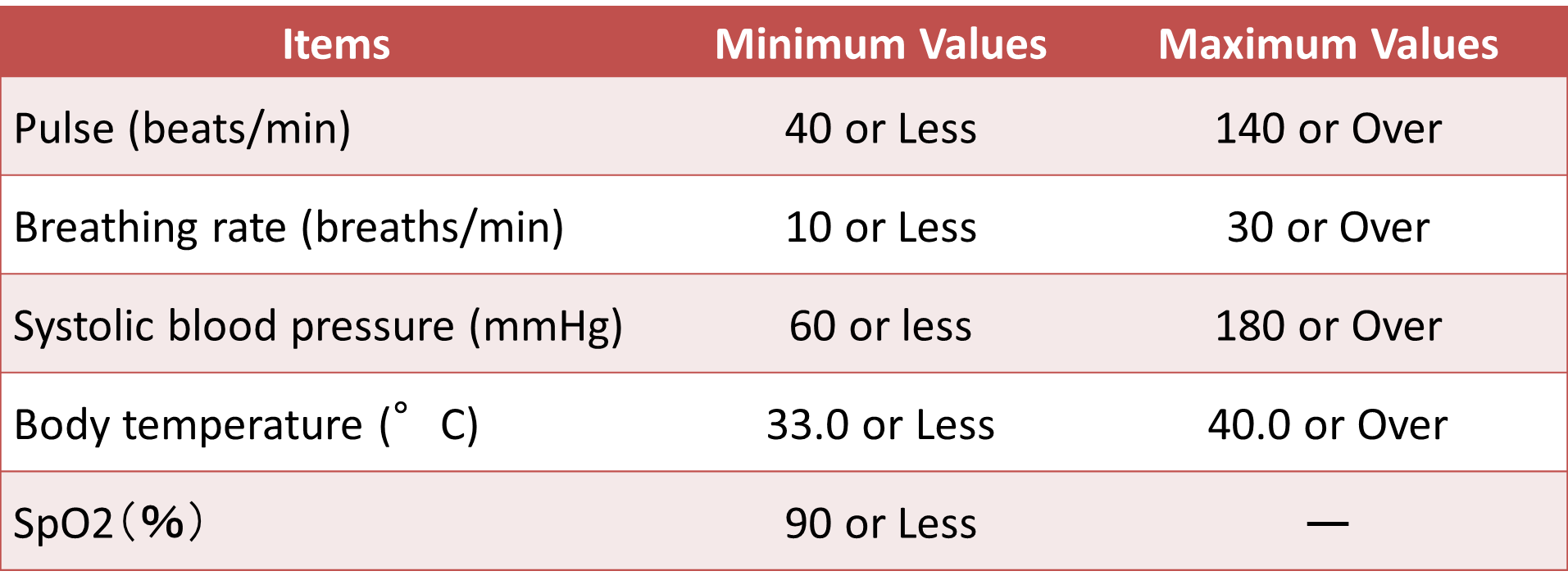
Standard values for each item when life is in danger (for adults)
These values are just a references, so don’t just judge all by only the measured values, but judge comprehensively, such as how different it is compared to usual patient’s condition.
Remember, if any vales are out of standard values, you have to report to doctor immediately.
Pulse Measurement
The pulse is generally measured at the radial artery in the wrist, but it may be measured at the carotid artery or armpit if the blood pressure is extremely low.
In addition, the Visiting Nursing often uses a “Pulse Oximeter” to simply measure the pulse.
With this single device, you can measure the patient’s pulse rate and SpO2 at the same time.
However, some experts point out the accuracy of using the Pulse Oximeter measurement results, so if you want to measure the pulse more accurately, measure it from wrist or neck.
Respiration Measurement
When measuring respiration rate, it is important to measure it in a relaxed state without making the patient aware that it is being measured.
The measurement method counts the cycle of “inhaling and exhaling” as one cycle, and measures for 1 minute while watching the movement of the chest and abdomen.
For adults, the normal range is 12 to 20 breaths per minute.
Blood Pressure Measurement
After the patient moves, the blood pressure will be high, so let the patient calm down for about 5 minutes and measure blood pressure later.
Also, when measuring it , have the patient sit down or lie down and rest quietly, and measure by the upper arm.
Since blood pressure varies slightly depending on the posture of patient, it is effective to measure in the same position and at the same site so that changes can be seen under the same conditions as the previous measurement.
Body Temperature Measurement
Ideally, the body temperature should be measured in the deepest part of the armpit.
The nurses usually use a Pulse Oximeter for simple measurement, or a Non-Contact Thermometer.
As with the measurement of blood pressure, if you always measure under the same conditions, you will be able to see the differences, so you need to do it in a way that puts less burden on the patient.
SpO2 Measurement
SpO2 (percutaneous arterial oxygen saturation) is the ratio of hemoglobin in the blood bound to oxygen.
Under normal conditions, approximately 96-99% of hemoglobin is bound to oxygen.
SpO2 is generally measured simply using a Pulse Oximeter.
Urine Volume Measurement
Urine volume is calculated by the amount of urine produced “per hour” or “per day”.
A normal urine volume of adult is around 1,200 to 1,500 ml/day. Carefully watch the patient if urine volume is excessive because of leading to dehydration.
Points to Remember When Measuring Vital Signs

The following points should be kept in mind when measuring vital signs.
1. Check the patient’s facial expression before measurements
2. Understand the difference between “pulse pressure” and “pulse tension”
3. Understand “Saturated Oxygen Level”
Let’s understand step by step.
Check the patient’s facial expression before measurements
Before measuring vital signs, check the patient’s facial expressions.
The purpose of vital signs is to objectively judge the patient’s condition from measurement data, but for physical assessment, information such as the atmosphere and discomfort you felt as a nurse will become also very important information.
Understand the difference between “pulse pressure” and “pulse tension”
Understand the difference between “Pulse Pressure” and “Pulse Tension” when measuring vital signs.
“Pulse Pressure” is grasped by “Systolic Blood Pressure” minus “Diastolic Blood Pressure”.

From this pulse pressure, we can grasp the stiffness and flexibility of the artery to some extent.
On the other hand, “Pulse Tension” refers to the strength of the pulse itself.
By measuring the strength of pulse, you can know approximate blood pressure.
A certain amount of experience is required to judge the tension of the pulse, but you should be able to understand it as “normal”, “strong”, or “weak” compared to usual.
Understand “Saturated Oxygen Level”
Understand the “Saturated Oxygen Level” correctly.
Oxygen Saturation is the percentage of hemoglobin bound to oxygen.
When measuring arterial blood, it is expressed as “SaO2”, and when measuring with a pulse oximeter, it is expressed as “SpO2”.
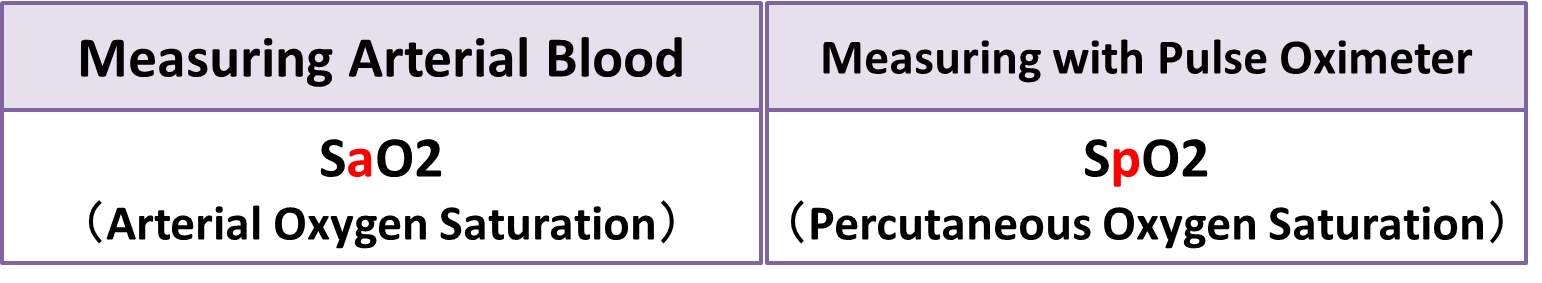
This value is normally around 95 to 99%, but if the hemoglobin value is lower in the first place than usual.
But it cannot be said that “there is enough oxygen” even if the saturation oxygen level is high, so be careful.
Also Remember About Important Vital Signs Items

I will explain the terms that you should keep in mind when measuring vital signs.
・Vital Reverse
・Delta pulse rate 20 rule
・The difference between “Pulse Rate” and “Heart Rate”
Especially two items for vital signs of “Vital Reverse” and “Delta Pulse Rate 20 Rule” are generally common words at Home Nursing.
I will explain them one by one.
Vital Reverse
The word “Vital Reverse” is defined as a state in which the pulse rate (heart rate) exceeds the systolic blood pressure.
This state is also called the “Pre-Shock State” and is the onset of shock.
This can be caused by sepsis, dehydration, or bleeding, but in any case, you should contact the doctor soon for advice.
Delta pulse rate 20 rule
The “Delta Pulse Rate 20 Rule” means a common rule that the pulse rate (heart rate) normally increases by 20 beats/minute for every 1°C increase in body temperature.
If a bacterial infection is suspected, an increase in the pulse rate of 20 beats/minute or more increse per 1°C rise in body temperature can be confirmed.
For example, a patient with a normal pulse rate of 65 beats/minute and a body temperature of 36.5°C, if the body temperature rises by 1°C and the pulse rate rises to 135 beats/minute, the patient should be suspeceted by bacterial infection.
In any case, if you discover this condition, contact doctor immediately.
The difference between “Pulse Rate” and “Heart Rate”
“Pulse Rate” is the number of times the blood vessels in the body beat in one minute.
On the other hand, “Heart Rate” is the number of times the heart beats in one minute.
It’s basic knowledge, but it’s important to understand the difference correctly.
In a normal person with no arrhythmia, when the heart beats once, it is transmitted as a pulse to the blood vessels of the body, so the Heart Rate and the Pulse Rate are basically the same.
Case Study and Countermeasures When Measuring Vital Signs

When measuring vital signs in a Home Nursing, there are times when the situation is such that the nurse has lost.
with the following cases, I will explain “What should I do in this case ?”.
1. When checking vital signs immediately
2. When the pulse is hard to recognize in the radial artery
3. When blood pressure cannot be measured in the upper extremities
4. When there is respiratory arrhythmia
5. When SpO2 cannot be measured
6. When the thermometer cannot be clamped
7. When the body temperature is high despite of good physical condition
In order not to panic when these situations occur, I will explain each cases and how to deal with it and respond flexibility.
When checking vital signs immediately
At the patient home as a Home Nursing, there is a cases that we need to check vital signs immediately.
At that time, the wrist (radial artery) and neck (carotid artery) can be used to predict systolic blood pressure.
Specifically, if you can feel the pulse when measuring with the wrist, you can determine that patient’s systolic blood pressure is around 80mmHg.

Also, if you can feel the pulse when measuring at the nape of the neck, you can assume that the patient has about 60mmHg.
Do not forget to also check for fever at this time.
When the pulse is hard to recognize in the radial artery
In some patients, it may be difficult to find a pulse at the wrist (radial artery).
At this time, you need to measure it in the carotid artery.
If the pulse is irregular, you can accurately measure the pulse by counting while listening to the heart sound (first sound at the apex) with a stethoscope.
The sound when the atria contract and blood fills the ventricles, the atrioventricular valves (mitral and tricuspid) close, and the ventricles begin to contract.
Since the first sound coincides with the pulse, it is suitable for measurement when the pulse of the radial artery is irregular.
When blood pressure cannot be measured in the upper extremities
When measuring blood pressure in the upper body, if there is swelling or injury, or if the patient complains of pain, there is a method of measuring in the lower extremities.
When measuring blood pressure in the lower extremities, use a thicker manchette because if the manchette is too narrow, the blood pressure value will be measured high.
When there is respiratory arrhythmia
“Respiratory Arrhythmia” is a condition in which the heart rate increases with inspiration and decreases with expiration.
In this case, ask the patient to temporarily hold the breath before the measurements.
Less than 10% of respiratory arrhythmias are generally not considered abnormal.
When asking the patient to hold the breath, be careful not to burden the patient.
When SpO2 cannot be measured
When measuring SpO2 with a pulse oximeter, if the result is not displayed easily, try measuring with another finger of the patient.
This is due to the different blood vessels in different fingers, and it may be possible to measure correctly with different fingers.
In the following cases that SpO2 cannot be measured in any other way, try the following methods.

The reasons not to able to measure SpO2 is probably simple problem.
Please try to above tips at that time.
When the thermometer cannot be clamped
For thin patients, the thermometer may not fit under the armpit or may not adhere to the armpit.
At this time, try to measure by sandwiching thermometer between the wrinkles of the abdomen.
It may not be possible to measure correctly if it is not pinched firmly, so try to make it as close to the skin as possible.
When the body temperature is high despite of good physical condition
If the patient seems to be feeling well but has a high temperature, it may be depression.
In particular, elderly patients may have a dull sense of temperature, and may not be able to dissipate their body temperature because they may wear excessive clothing or set the air conditioning to hotter.
At this time, try to measure after adjusting the room temperature and their clothes.
Conclusion

In this time, I explained the measurement of vital signs in detail.
The contents of this time are all the basic business in Home Nursing, and it’s all about the knowledge that is useful to know.
Let’s review this page many times and put it into practice.
I hope you become a good nurse standing by all patients.




